According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, approximately 20.4% of businesses fail within their first year, and about 49.4% fail within the first five years.
A primary reason behind these failures is operational inefficiency—wasted resources, slow activities, and poor process management that eat into profitability. Businesses risk falling behind without a clear understanding of where these issues lie.
Regular operational audits provide the insight needed to stay competitive. Companies can identify inefficiencies, eliminate unnecessary costs, and enhance overall performance by systematically assessing workflows, resource allocation, and compliance. Making operational audits a regular part of your business strategy ensures continuous improvement, resilience, and long-term success.
In this blog, we will discuss the importance of regular operational audits, their main benefits, and how they help businesses improve efficiency, reduce risks, and drive long-term success.
What is an Operational Audit?
An operational audit systematically reviews a company’s processes, procedures, and systems to assess efficiency, effectiveness, and compliance. They evaluate overall business operations to identify inefficiencies, risks, and areas for improvement.
This type of audit examines workflows, resource allocation, internal controls, and adherence to industry standards. Its goal is to improve productivity, reduce waste, and ensure that business functions align with strategic objectives. Regular operational audits help organizations stay competitive, improve decision-making, and maintain regulatory compliance.
The Importance of Investing in Operations
Operations often take a backseat to other business priorities. While companies invest heavily in marketing, sales, and product development, operational efficiency is frequently overlooked. For most small and mid-sized companies, optimizing operations is less about automation and more about ensuring every resource is used effectively.
Many businesses fail to invest in operations because they are unsure where to start or what will yield the greatest impact. As a result, inefficiencies grow over time, leading to wasted resources, increased costs, and slowed business growth. Without a clear strategy for operational improvement, companies risk stagnation and missed opportunities.
Conducting an operational audit helps businesses make smarter investments in efficiency. By identifying weak points in workflows, companies can allocate resources more effectively, improving productivity and long-term profitability. Instead of reacting to operational challenges when they become costly problems, companies can proactively streamline processes, enhance compliance, and reduce unnecessary expenses.
A strong operational foundation is essential for sustainable business growth. Without it, even the most promising businesses may struggle with scalability, customer satisfaction, and cost management. An operational audit comprehensively analyzes business processes, helping leaders pinpoint inefficiencies and implement targeted improvements.
Benefits of Regular Operational Audits
Regular operational audits offer several advantages that contribute to a company’s long-term success. These benefits include:
- Improved Efficiency: Operational audits identify workflow bottlenecks, redundancies, and inefficiencies. Businesses can streamline processes, optimize resource allocation, and enhance productivity by addressing operational efficiency issues.
- Cost Savings: Audits help discover unnecessary expenses, wasteful practices, and underutilized resources. Businesses can use these insights to cut costs without compromising quality or performance.
- Better Compliance: Regular audits ensure adherence to industry regulations, company policies, and legal requirements. This reduces the risk of penalties, lawsuits, and reputational damage caused by non-compliance.
- Better Risk Management: Audits help detect operational risks, such as security vulnerabilities, supply chain disruptions, and internal fraud. Addressing these risks proactively minimizes potential losses and strengthens business resilience.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Businesses can make informed decisions backed by data by analyzing audit findings. This improves strategic planning, goal-setting, and resource allocation for long-term success.
- Stronger Internal Controls: Operational audits evaluate internal controls and identify gaps that could lead to errors or fraud. Strengthening these controls enhances accountability, transparency, and governance.
- Increased Employee Productivity: Clear processes and reduced inefficiencies enable employees to focus on high-value tasks. A well-structured work environment leads to higher engagement, better performance, and improved job satisfaction.
- Competitive Advantage: Continuous process improvements gained through regular audits help businesses adapt to market changes, enhance customer satisfaction, and maintain an edge over competitors.
Steps Involved in an Operational Audit
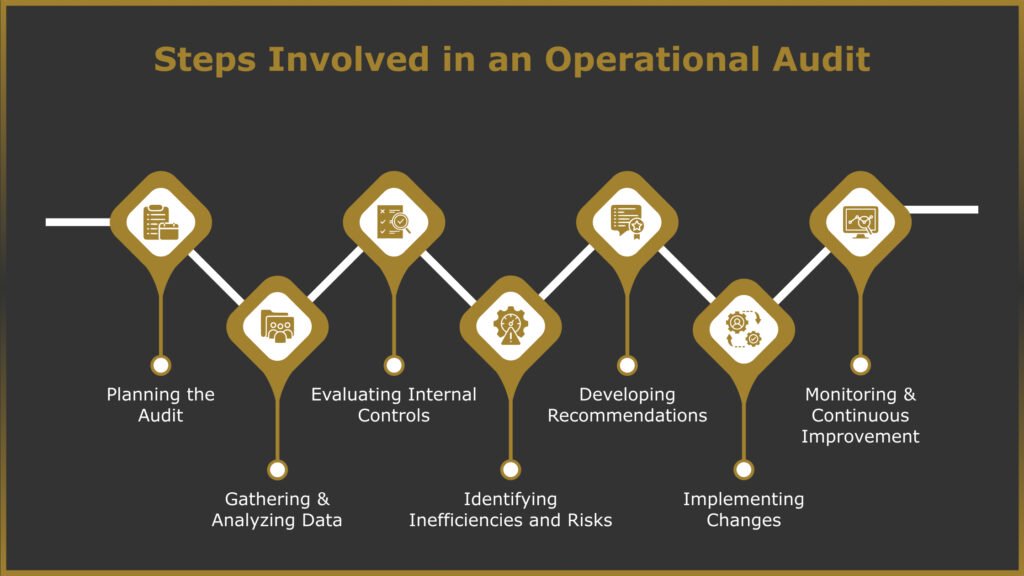
Conducting an operational audit requires a structured approach to ensure a thorough evaluation of business processes. Each step helps identify inefficiencies, assess compliance, and implement necessary improvements. The major steps involved in an operational audit include:
1. Planning the Audit
The first step in an operational audit is defining its scope and objectives. Businesses must determine which departments, processes, or operations will be reviewed. Establishing clear goals ensures the audit remains focused on identifying inefficiencies, compliance gaps, or areas for improvement.
2. Gathering & Analyzing Data
Auditors collect relevant data, including financial reports, workflow documentation, performance metrics, and employee feedback. This data provides insights into how processes function and highlights inconsistencies or inefficiencies that may need correction.
3. Evaluating Internal Controls
Assessing internal controls ensures that policies and procedures align with regulatory requirements and business objectives. This step helps identify weaknesses in oversight, workflow management, and risk mitigation strategies.
4. Identifying Inefficiencies and Risks
The audit identifies bottlenecks, redundancies, and potential compliance risks through data analysis and internal control evaluation. These insights form the basis for recommendations on improving productivity and operational effectiveness.
5. Developing Recommendations
After identifying issues, auditors propose actionable solutions to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve internal processes. These recommendations should be practical, measurable, and aligned with business goals.
6. Implementing Changes
Management reviews the audit findings and decides on the best course of action. Implementation may involve revising workflows, updating policies, investing in technology, or providing additional employee training.
7. Monitoring & Continuous Improvement
An operational audit is not a one-time activity. Regular follow-ups and continuous monitoring help ensure that implemented changes lead to sustained improvements. Businesses should schedule periodic audits to optimize operations and align with evolving goals.
How Can a Fractional COO Help with Operational Audits?
A fractional COO provides executive-level expertise without full-time costs, making them an ideal resource for conducting operational audits. Their strategic oversight ensures that audits exceed compliance checks and drive meaningful improvements. Here’s how a Fractional COO can support operational audits:
- Unbiased Assessment: Internal teams may overlook inefficiencies due to familiarity with existing processes. A Fractional COO brings an objective perspective to identify gaps, redundancies, and missed opportunities.
- Comprehensive Process Evaluation: With experience across multiple industries, a Fractional COO can analyze workflows, resource allocation, and bottlenecks to pinpoint areas that need optimization.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: They implement key performance indicators (KPIs) and use data insights to measure operational effectiveness, ensuring decisions are based on concrete evidence rather than assumptions.
- Strategic Implementation of Improvements: Beyond identifying issues, a Fractional COO helps with actionable business development solutions and ensures they are implemented effectively. They work with teams to streamline processes, reduce inefficiencies, and enhance productivity.
- Cost Optimization and Resource Allocation: By evaluating costs, supply chain efficiency, and workforce utilization, a Fractional COO ensures that resources are allocated effectively, improving profitability without sacrificing quality.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: An operational audit is not a one-time fix. A Fractional COO establishes ongoing monitoring systems to ensure continuous improvement, adapting strategies as business needs evolve.
- Scalability and Growth Planning: For businesses aiming to scale, a Fractional COO ensures that operational systems can support expansion, preventing inefficiencies that could hinder growth.
Businesses can turn operational audits into a strategic advantage, ensuring that improvements are sustainable and aligned with long-term goals by leveraging the expertise of a Fractional COO.
Also read: Why Should You Consider Fractional Sales Leadership for Business Success?
Eliminate Operational Inefficiencies with Outcomes COO

Operational inefficiencies can slow growth, increase costs, and limit business potential. Regular operational audits provide the insights needed to optimize processes, enhance efficiency, and maintain a competitive edge.
Outcomes COO offers expert Fractional COO services to help you assess, improve, and streamline your operations without the cost of a full-time executive. Whether you need a strategic audit, process improvements, or long-term operational planning, we provide the leadership and expertise to drive measurable results.
Take the next step toward operational excellence. Optimize your business and unlock sustainable growth.
FAQs
1. How often should a business conduct an operational audit?
The frequency depends on the company’s size, industry, and operational complexity. Many businesses conduct audits annually, but those in fast-changing industries or with compliance requirements may benefit from quarterly or biannual audits.
2. What’s the difference between an operational audit and a financial audit?
An operational audit evaluates business processes, efficiency, and effectiveness, whereas a financial audit examines a company’s financial statements to ensure accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. Both audits serve different but complementary purposes.
3. What role does technology play in operational audits?
Technology helps businesses collect and analyze data more efficiently, automate processes, and implement real-time monitoring systems. Digital methods like ERP systems, AI-driven analytics, and process automation software improve audit effectiveness.
4. What challenges do companies face when conducting an operational audit?
Common challenges include resistance to change, lack of clear audit objectives, limited access to accurate data, and difficulty implementing recommended improvements. Having executive support and a structured approach can help overcome these issues.

